Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is CNC Turning?
CNC Turning, or Computer Numerical Control Turning, is a manufacturing process used to shape cylindrical or conical parts from materials like metal, plastic, or wood. It’s done with the help of a computer-controlled machine called a CNC lathe. This machine spins the material while a cutting tool removes excess material, creating the desired shape. CNC turning is widely used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and engineering to produce things like screws, shafts, and custom components with high precision. It’s a fast and efficient way to make parts that need to be very accurate and have a round or tapered shape.
What is CNC Turning Service?

A CNC Turning Service is a machining service that utilizes CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology to conduct precision turning operations on a workpiece. CNC turning involves the use of a specialized machine known as a CNC lathe, which is programmed to rotate the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material to produce cylindrical or conical shapes. This service is widely employed in manufacturing and engineering to fabricate various components and parts with a high degree of accuracy.
A CNC Turning Service is like having a super-precise machine that can make cylindrical or cone-shaped parts from materials like metal or plastic. It works by spinning the material while a special tool shapes it. This is great for making things like screws, rods, or even custom parts. It’s fast, accurate, and can be used for both one-of-a-kind items and big batches. It’s like having a master craftsman create the same thing over and over with perfect precision.
How do CNC Turning Machines work?
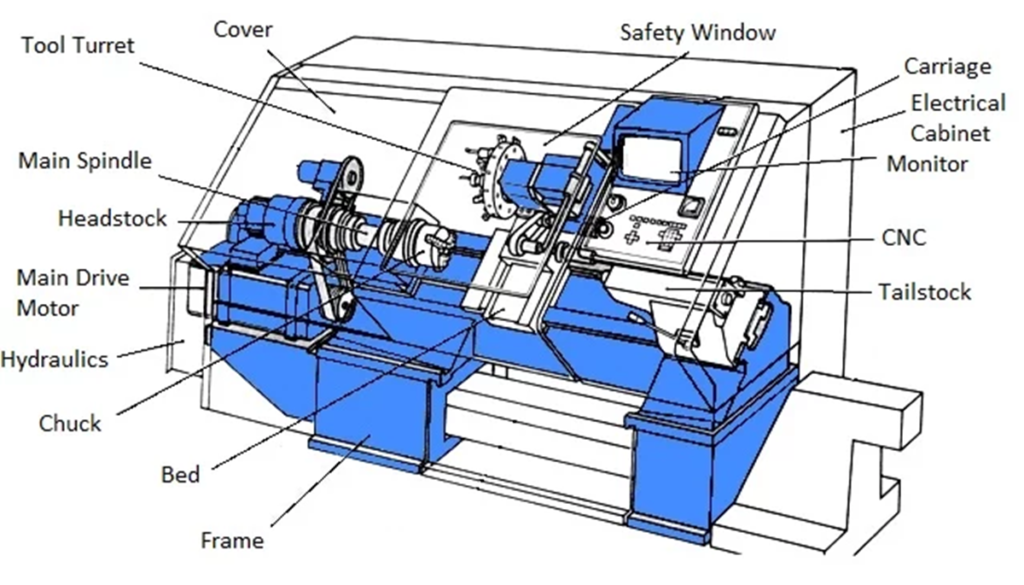
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning machines are sophisticated pieces of equipment used in the manufacturing industry to create precision-machined components. These machines operate by following a set of computer-generated instructions to turn a workpiece and remove material from it with exceptional accuracy. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how CNC turning machines work:
- Workpiece Preparation: The process begins with the preparation of a raw workpiece, which is usually a cylindrical or rod-like piece of material, such as metal or plastic. The workpiece is securely mounted on a spindle, which rotates it during the machining process.
- Tool Selection: Selecting the appropriate cutting tool is crucial for the machining process. The choice of tool depends on factors like the material of the workpiece, the desired precision, and the specific features to be created.
- Computer Programming: Before machining begins, a CNC program is created. This program is a set of detailed instructions that guide the CNC turning machine in the entire process. It specifies parameters like the toolpath, cutting speed, and depth of cuts. Skilled programmers use Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software to create this program.
- Precision Turning: Once the CNC program is loaded into the machine’s control system, the machining process begins. The spindle rotates the workpiece, while the cutting tool moves along the programmed path. The tool removes material from the workpiece in a controlled and precise manner. The cutting tool may move along multiple axes, allowing it to create complex shapes and features on the workpiece.
- Constant Monitoring: Throughout the machining process, the CNC turning machine continuously monitors the position and performance of the cutting tool. It makes real-time adjustments to ensure that the tool stays on the intended path and that the desired tolerances are maintained.
What More CNC Turning Machines work?
1. Producing a CAD model
Producing a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model is a fundamental step in the design and engineering process, whether for manufacturing, architecture, or various other applications. CAD modeling involves creating a detailed digital representation of an object or system using specialized software. Here’s an overview of the steps involved in producing a CAD model:
Conceptualization and Planning: The first step in creating a CAD model is to define the project’s goals and requirements. This involves understanding the purpose of the model, its intended use, and any specific design parameters or constraints. The conceptualization phase includes brainstorming ideas and sketching initial concepts.
Gathering Data and Specifications: To accurately represent the object or system in the CAD model, it’s essential to gather all relevant data and specifications. This may include measurements, technical drawings, photographs, or any existing physical prototypes.
Selecting CAD Software: Choose the appropriate CAD software that suits the specific project requirements. CAD software comes in various forms, from 2D drafting tools to sophisticated 3D modeling applications. The choice of software depends on factors like the complexity of the design.
2. Convert CAD model for CNC machine
Converting a CAD model for use with a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine is a crucial process that allows the digital design to be transformed into a physical object with precision. CNC machines, such as CNC mills and CNC lathes, rely on CAD models to guide their machining operations. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to convert a CAD model for CNC machining:
Select the Appropriate File Format: Start by ensuring that your CAD model is saved in a compatible file format that the CNC machine can read. Common formats include STL, STEP, IGES, and DXF. Check the CNC machine’s specifications to confirm which format it supports.
Import the CAD Model into CAM Software: CNC machines require specific instructions for toolpaths and operations, which are generated using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. Import your CAD model into CAM software, which will allow you to generate toolpaths and convert the design into machine-readable code.
Define the Workpiece and Stock Material: In the CAM software, specify the workpiece material and dimensions. This information helps the software calculate toolpaths and cutting parameters based on the material’s properties.
3. Starting the turning process
Starting the turning process on a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathe is a crucial step in manufacturing precision components. CNC lathes are highly automated machines used to create cylindrical or conical shapes by rotating a workpiece while a cutting tool removes material. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to initiate the turning process:
Workpiece Installation:
Begin by securing the raw workpiece onto the lathe’s spindle. The workpiece should be centered and clamped securely to ensure stability during the turning process.
Tool Selection: Choose the appropriate cutting tool based on the material of the workpiece, the desired precision, and the specific features to be created. Tools may vary in shape, size, and material, and the choice will impact the quality of the turned part.
Tool Setting and Alignment:
Precisely set the tool’s position and alignment. This includes ensuring the tool’s cutting edge is at the correct height and angle relative to the workpiece. Use the lathe’s built-in measuring and alignment tools to achieve this.
What is the difference between CNC milling & turning
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling and CNC turning are two distinct machining processes used to create precise parts and components, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Here are the key differences between CNC milling and CNC turning:
Type of Operation: CNC Milling: In milling, the cutting tool rotates and moves along multiple axes (typically X, Y, and Z) to remove material from the workpiece. Milling is primarily used to create features like slots, holes, pockets, and complex 3D shapes.
CNC Turning: Turning involves rotating the workpiece while a stationary cutting tool removes material. It primarily produces cylindrical or conical shapes, such as shafts, pins, and rings.
Workpiece Shape:
CNC Milling: Milling is ideal for workpieces with flat or irregular surfaces and those that require complex contours and shapes.
CNC Turning: Turning is suited for workpieces that are primarily cylindrical or conical in shape.
Tool Movement:
CNC Milling: Milling tools have multiple cutting edges and rotate during the operation. They can move in various directions to cut material from multiple angles.
CNC Turning: Turning tools are typically single-point tools and remain stationary during the operation. They remove material as the workpiece rotates.
Tool Types:
CNC Milling: Milling tools include end mills, face mills, and ball-nose cutters, among others, to create diverse shapes and features.
CNC Turning: Turning tools include various inserts and tool bits designed for operations like facing, grooving, and threading.
Operations:
CNC Milling: Milling can perform a wide range of operations, including contouring, drilling, slotting, and pocketing, making it suitable for complex parts.
CNC Turning: Turning primarily performs operations like facing, turning, boring, and threading, which are common in cylindrical components.
Workpiece Holding:
CNC Milling: The workpiece is usually held in a vice or fixture and secured to the milling table.
CNC Turning: Workpieces are secured in a chuck or collet, which rotates the part during the turning process.
Materials and Tolerances:
CNC Milling: Milling is suitable for various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. It can achieve tight tolerances and surface finishes.
CNC Turning: Turning is ideal for cylindrical components and is commonly used for materials like metals, plastics, and ceramics. It can achieve precise roundness and concentricity.
Applications:
CNC Milling: Milling is versatile and commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and tool and die making for complex and intricate parts.
CNC Turning: Turning is often applied in industries like manufacturing, machining, and the production of components with rotational symmetry.
Tool Changes:
CNC Milling: Milling machines can have multiple tools in a tool changer, allowing for the automatic switching of tools during a job.
CNC Turning: Turning machines often have fewer tool changes as they primarily use single-point cutting tools.
Both CNC milling and CNC turning are essential in modern manufacturing and play distinct roles in producing a wide range of components. The choice between them depends on the specific part’s geometry, material, and required features. Manufacturers often use both processes in conjunction to create complex, high-precision parts
What is Petron Thermoplast CNC Turning Service?

Petron Thermoplast CNC Turning Service is a precision machining process offered by Petron Thermoplast, a leading name in the world of manufacturing and engineering. This service is a crucial component of their wide range of solutions aimed at providing high-quality machined components to various industries.
Understanding CNC Turning Services
CNC turning is the process of fabricating parts by rotating a workpiece on a spindle while a cutting tool precisely removes material. This precision machining technique allows for the creation of parts with tight tolerances, making it a preferred choice in industries that require complex components.
What Sets Petron Thermoplast Apart?
Petron Thermoplast prides itself on its commitment to quality, precision, and innovation. Their CNC Turning Service stands out due to its dedication to producing components that adhere to the strictest specifications. Whether you require a one-off prototype or a large production run, Petron Thermoplast has the expertise to deliver.
The CNC Turning Process
CNC Turning involves several steps, including:
1. Workpiece Preparation
Before the CNC machine can start turning, the workpiece must be properly secured to the spindle.
2. Tool Selection
Selecting the right tool, with factors like material and precision in mind, is crucial.
3. Programming
A CNC program is created to guide the machine throughout the turning process.
4. Precision Turning
The CNC machine carries out the turning process with unparalleled accuracy and repeatability.
5. Quality Inspection
The finished component is thoroughly inspected to ensure it meets the desired specifications.
Materials Used in CNC Turning
CNC Turning can be applied to various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. Petron Thermoplast is adept at working with a diverse range of materials to cater to the specific needs of its clients.
Benefits of Petron Thermoplast CNC Turning Service
The benefits of choosing Petron Thermoplast CNC Turning Service include:
Precision: Their CNC machines ensure parts are manufactured with the utmost precision.
Speed: The automated process increases production efficiency.
Customization: Petron Thermoplast can tailor solutions to meet unique requirements.
Cost-Effective: Offering competitive prices without compromising quality.
Reliability: Proven track record in delivering high-quality components.
Quality Control and Precision: Quality control is at the core of Petron Thermoplast’s CNC Turning Service. They utilize advanced inspection tools to ensure that each component meets the required specifications, leaving no room for errors.
Industries Benefiting from CNC Turning: CNC turning plays a vital role in several industries, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics. Its versatility and precision make it an indispensable technology for various applications.
How to Avail Petron Thermoplast CNC Turning Service
To avail of this service, you can contact Petron Thermoplast through their website or customer service. They will work with you to understand your requirements and provide a customized solution that fits your needs.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications to illustrate the capabilities of Petron Thermoplast CNC Turning Service, here are some real-world case studies showcasing their successful projects in different industries.
Cost-Effective Solution: Petron Thermoplast offers a cost-effective solution without compromising on the quality and precision of components. Their competitive pricing makes them a preferred choice for businesses of all sizes.
Sustainability Initiatives: Petron Thermoplast is committed to sustainability and minimizing their environmental footprint. They use eco-friendly materials and processes wherever possible, aligning with the growing global focus on sustainability.
Future Prospects: The CNC Turning industry is constantly evolving, and Petron Thermoplast keeps pace with the latest advancements in technology and techniques. Their commitment to innovation ensures that their services will continue to meet the ever-changing needs of various industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Petron Thermoplast CNC Turning Service is a beacon of precision and quality in the manufacturing world. Their commitment to delivering components with exceptional precision, on-time delivery, and competitive pricing makes them an industry leader.
Frequently Asked Questions
What materials can Petron Thermoplast CNC Turning Service work with?
Petron Thermoplast can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
How do I request a quote for CNC Turning services from Petron Thermoplast?
You can easily request a quote by contacting Petron Thermoplast through their website or customer service.
What industries benefit the most from CNC Turning services?
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics greatly benefit from CNC Turning services due to their precision and versatility.
Is Petron Thermoplast committed to sustainability?
Yes, Petron Thermoplast actively participates in sustainability initiatives and uses eco-friendly materials and processes wherever possible.
How does Petron Thermoplast ensure the quality of its CNC turned components?
Petron Thermoplast employs advanced inspection tools and a rigorous quality control process to ensure the components meet the required specifications.
You May Also Like : How CPVC Pipes are Revolutionizing the Industry, Georg Fischer Piping Systems

