- ABS
- Acetal Sheet
- Acrylic & Perspex
- Dry Wipe Board
- Engraving Plastic
- Mirrored Plastic Sheet
- Nylon 6
- Nylon 66
- PEEK Sheet
- PEI (Ultem)
- PET
- PET (Ertalyte)
- PETG
- Plastic Shims
- Polycarbonate
- Playground Plastic (HDPE)
- Polyethylene PE300 - HDPE
- Polyethylene PE500 - HMWPE
- Polyethylene PE1000 - UHMW
- Polypropylene
- Prismatic Diffuser Panels
- PTFE
- PVC
- PVC Foam (Foamex)
- PVDF
- Salbex Pressed PVC
- Vespel
- Vyon Breathable Plastic
- Metal Detectable Plastic
- Tufnol Industrial Laminates
- Glass Based Laminates

Product Description
PVDF sheet has strong chemical resistance as well as good mechanical, thermal, and electrical qualities. It offers strong UV, corrosion, and radiation resistance and may be utilised in food contact applications. It is also a versatile engineering material due to its high wear resistance and sliding qualities.
Electrical wire and cable insulation, medical packings, anti-corrosion linings, corrosion resistant diaphragms, pipe-lining for corrosive liquids and gases, sliding components and agitators are some of the applications.
Applications
- Electrical wire and cable insulation, medical packings, anti corrosion linings, corrosion resistant diaphragms, pipe-lining for corrosive liquids and gases, slide parts and agitators.
Key Features
- Temperature range: -30°C to +140°C (150°C in the short term).
- Excellent UV and weather resistance;
- Excellent electrical insulation qualities.
- High purity and chemical resistance.
- Excellent wear resistance.
- Excellent weldability; FDA-approved for food contact.
Availability
Also available: PVDF Rod.
| Sheet Size (mm) | Sheet Thickness (mm): |
|---|---|
| – | 8 10 12 16 20 25 30 40 50 60 |
| 3000 x 620 | * * * * * * * * * * |
*Indicates the availability of standard sheets.
Please enquire if you want other sheet sizes or thicknesses.
There may be a minimum order quantity.
Product Images
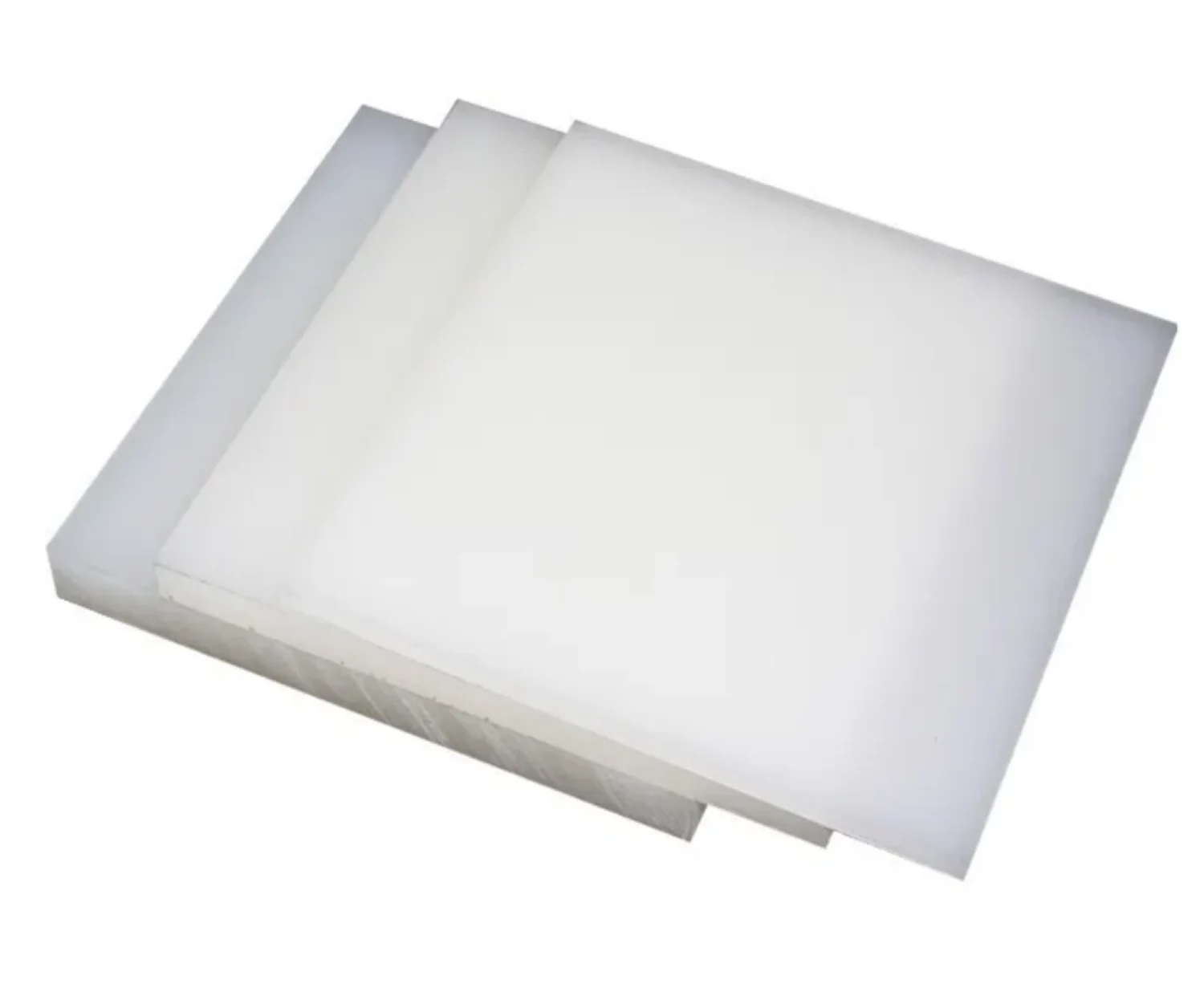
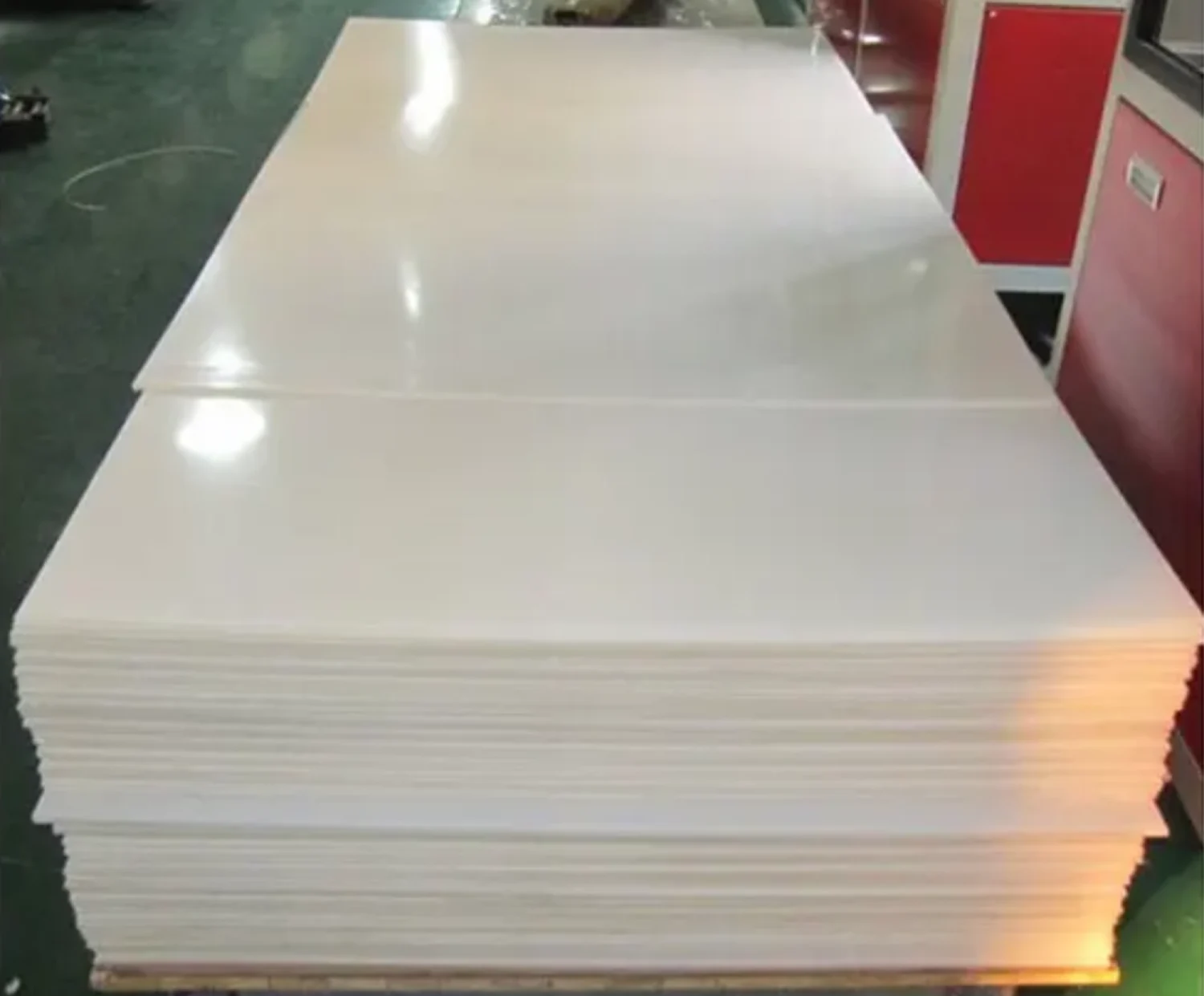
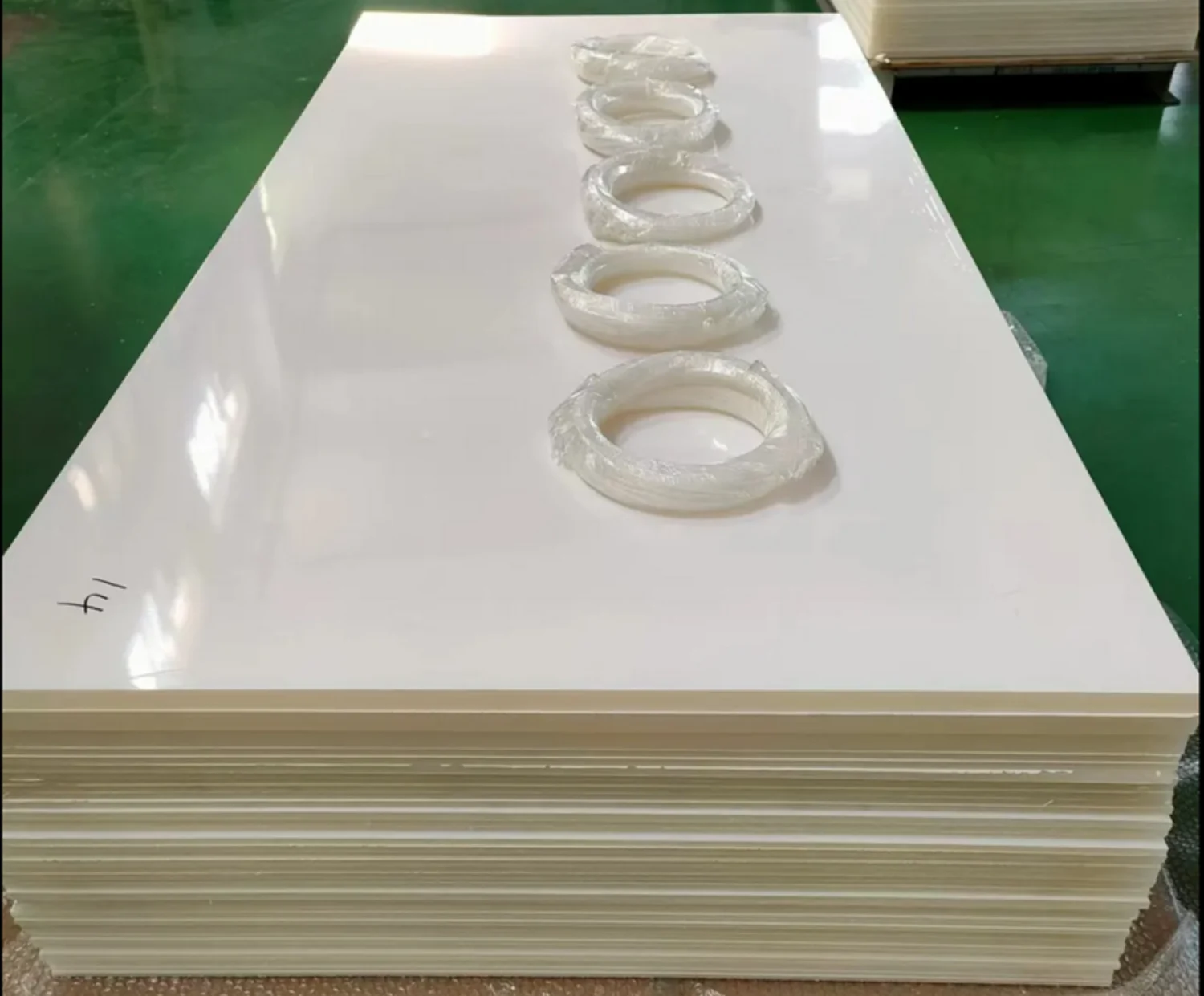




PVDF Sheet Properties And Various Applications
Polyvinylidene Fluoride is often known as Polyvinylidene Difluoride (PVDF). It is a thermoplastic fluoropolymer that is highly non-reactive. The polymerisation of Vinylidene Difluoride forms it. PVDF is a speciality plastic used in various applications that require high purity and inertness to solvents, acids, and bases. PVDF sheet is made from it, and it has numerous applications. PVDF is available in fine powder form on the market and is used in elevated metal and cement paints.
PVDF in different forms:
PVDF in semiconductors:
High purity PVDF for Semiconductors PVDF resin grades meet industry demands as semiconductor products demand more pure materials. As a result, PVDF resin is suitable for protective sheathing, plenum, and communication system applications. Hence, it finds extensive use in the semiconductor industry.
PVDF coating:
These coatings are durable because they use greater pigments, and one of the strongest bonds identified is the carbon-fluorine bond.
PVDF in EV batteries:
PVDF resin is used in both private and public vehicles. In industry, it can be used as a barrier liner for automotive fuel lines and gas station fuel pipes, as decorative films, and as a binder in HEV/EV batteries.
It is also used for weathering, anti-grime/graffiti protection, moulded and thermoformed body components, and tank trailer linings for corrosion protection.
PVDF sheet properties:
The properties of PVDF plastics are as follows.
- Recyclable
- Lightweight
- Toughness
- Weatherproofing
- Excellent heat resistance.
- Excellent electrical insulator
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Slick or low in coefficient of friction.
Special PVDF sheet industrial characteristics:
These include the followings.
- High creep and fatigue resistance.
- Thermal stability is outstanding.
- Radiation resistance is outstanding.
- It is frequently used as an insulation and UV protection cover in chemical applications (it does not age)
- The dielectric constant is extremely large.
- The temperature ranges from -20°C to +130°C.
PVDF applications:
- PVDF materials are widely used in the markets listed below:
- In the market for high-purity semiconductors,
- In the paper and pulp manufacturing industry,
- Nuclear waste processing,
- In general, in the chemical processing industry,
- Water treatment membranes, etc.
Standard size:
- Sheet dimension: 24 in X 48 in.
- Thickness is from 0.500 in to 4 in.
Why should you use PVDF sheets?
This sheet is widely used in applications where high purity, strength, and resistance to solvent and heat slow smoke generation are required. Compared to fluoropolymers, it is known for its low density and cost.
Furthermore, because of their ease of melting and low cost compared to others, these sheets are available in various piping products.
Petron Thermoplast, the best PVDF fittings manufacturers, made quality sheets that are resistant to high temperatures, have excellent chemical resistance, good electrical properties, and are wieldable.
We offer great quality PVDF sheet and PVDF pipes at the most competitive prices to our valued customers.
Know about PVDF plastic from Petron
Because it offers significant benefits over other polymers, such as strength, durability, abrasion resistance, low permeability, recyclable nature, and more, PVDF is a value-designed material.
Technically speaking, PVDF is a high-performance thermoplastic that is semi-crystalline. Fluoropolymers also include PVDF plastic. Fluoropolymers are polymers or plastics with several sections inside each molecule that are bound to fluorine. Solvents, acids, and bases are exceedingly difficult to penetrate fluoropolymer polymers.
Additionally, FDA-approved and fully non-toxic PVDF. It indicates that it can be used for recurrent food contact.
You may get advice on PVDF from Petron, the top thermoplastic producer in India.
Production of PVDF Plastic
Vinylidene difluoride, a monomer, is polymerized by free radicals to generate PVDF plastic (1,1-difluoroethylene). This procedure takes place in an environment with an emulsion between 10 and 150 °C and 10 to 300 atm of pressure.
Melt casting is used to process and build the PVDF material into components and coatings. It may also be treated from a solution using techniques including solution casting, spin coating, and film casting.
Melt casting involves heating a polymer until it melts, pouring it into a mold, allowing it to cool and solidify, and then removing it.
Solution casting creates porous polymer membranes by dissolving the polymer in an appropriate solution. The solubility of PVDF is largely dependent on the polarity, temperature, and molecular weight of the solvent.
Spin coating: To create piezoelectric thin film devices, the polymer is processed into thin films from the higher beta-phase by stretching, applying high pressure, or applying an electric field to the films.
Film casting: The polymer is treated into homogeneous, high-quality films or thin sheets using a customized extrusion operation. Extrusion of the film is another name for this procedure.
Properties of PVDF
Some of PVDF’s most distinguishing characteristics include:
- excellent resistance against abrasion
- stable thermal performance
- resistance to high-energy radiation and ultraviolet (UV) light
- high creep resistance under prolonged stress (creep)
- high level of fatigue resistance during cyclic loading
- high dielectric resistance
- resistance to most solvents and compounds
- Low water absorption; at normal temperature, it absorbs less than 5% water. Considered mechanically stronger than other fluoropolymers (i.e., PTFE)
Meets requirements for use in food processing (non-toxic and resistant to bacteria and fungi).
PVDF Material
If you want to explore the details of PVDF, this guide is for you to understand the facts. A semi-crystalline thermoplastic fluoropolymer is polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). It is easily melt-processible and may be made into pieces using compression and injection moulding. It combines good processability with great mechanical strength. Pumps, valves, pipes, tubes, and fittings used in chemical processing are frequently made of PVDF.
Recently, the polymer polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) has shown a lot of interest. It attracted interest because any commercial polymer has the strongest piezoelectric characteristics. The polymer is widely employed in high-tech applications, including electrical, electronic, specialized, and energy-related machinery for chemical processes. But why is PVDF a high-performance plastic in so many industries? Find out more by reading on. Petron Thermoplast will assure you about the complete guidance of PVDF.
If you are curious about learning PVDF Materials, it is important to learn what PVDF is:
What is PVDF?
PVDF is a semi-crystalline, high-purity thermoplastic fluoropolymer known as PVF2 or Polyvinylidene Fluoride or Polyvinylidene Difluoride. PVDF shows a strong combination of qualities at service temperatures up to 150°C, including:
outstanding chemical resistance
strong mechanically
pyroelectric and piezoelectric characteristics
In addition to being easily processed
The alternation of polar CH2 and CF2 groups on the polymer chain gives it its highly desirable insolubility and electrical characteristics.
PVDF is easily melt-processible and can be made into products using compression and injection molding. As a result, it is frequently and rapidly used in devices for chemical processing, including pumps, valves, pipes, tubes, fittings, sensors, and actuators.
Production Procedure of PVDF
1,1-difluoroethylene (CH2=CF2) is typically used as a starting material for the free radical polymerization of PVDF (homopolymers and copolymers). At a temperature of 10-150°C and a pressure of 10-300 atm, polymerization occurs in an emulsion or suspension. The resultant material is subsequently converted into film or sheets. The most popular methods for creating PVDF copolymers are chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE) or hexafluoropropylene (HFP).
Compared to PVDF homopolymer grades, PVDF copolymers with HFP have more flexibility.
With outstanding low-temperature performance and minimal shrinkage, copolymers with CTFE are some of the most flexible PVDF materials.
Applications requiring increased flexibility, such as wire, cable, and tubing, are perfect for copolymers. A PVDF material has several properties; they are:
Properties
The properties of PVDF include the following.
Typically, it is a polymer that is approximately 50% amorphous and semi-crystalline. It has a fairly regular structure, with relatively few monomer units connected head-to-head and most VDF units joined head-to-tail.
Phases are the four different potential conformations of this fluoroplastic.
The maximum dipole moment is obtained when all of the polymer’s dipoles are aligned in the same direction, which corresponds to the -phase of the PVDF. The C-F bonds are polar. The preferred phase for the polymer’s piezoelectric properties is the -phase.
The net polarization of crystallites is zero because their dipole moments are orientated in opposition to one another.
If you want to learn more information on PVDF materials, you may contact the professionals of Petron Thermoplast.
Related Products

PVDF Rod

Plastic Machining

