We live in a world of advanced technology that forms part of a world in which small machinery and complicated components are integrated into people’s daily lives. Be it gears integrated into your car or minute parts used in your electronic gadget, how does one wonder how such precise parts are made?
The technique used to produce most of the parts is generally summed up in one process, CNC precision machining. Computer numerical control has indeed taken modern industries to another level with its high-speed fabrication of parts. CNC machining does this a notch higher by ensuring unparalleled accuracy and easing the whole manufacturing process.
What is Precision Machining?
Precision machining is the performance of material removal where the products concerned are either complex or highly detailed. These products find themselves in the aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and electronic industries, among others. In a nutshell, precision machining is about making parts meet exact specifications with tolerances as close as a few microns.
Precision machining is intended to increase accuracy and efficiency in metal manufacturing.
Precision machining refers to the process of stock material conversion to precise dimensions and surfaces applied mainly to metal but also to many other materials, including plastics and composites, by the removal of small, controlled amounts of material. This is achieved with the aid of complex machinery and equipment of high technological capability, which are in some cases computer-numerically controlled for performing very intricate tasks with great precision.
Applications of Precision Machining
There is no shame in manufacturing where the accuracy, reliability, and quality may range from high to a higher tolerance. These include, among others:
- Aerospace: Manufacturing engine parts, landing gears, and structural parts is done.
- Automotive: The manufacturing of gear shafts, pistons, blocks, and other component parts.
- Medical Devices: Making implants, surgical tools, and diagnostic equipment.
- Electronics: Manufacturing circuit boards, connectors, device housings, and various other components.
- Military: Production of weapon systems, communications devices, and personal protective gear.
Advantages of Precision Machining
Precision machining is another name for producing parts of complex machinery with a higher standard than baseline CNC machining. It is an excellent solution to meet exact project requirements: Some of the benefits accrued to precision machining include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Accuracy : Extremely tight tolerances from which all parts are manufactured assure proper fit and operation in the intended application.
- Consistency: It provides uniformity from one identical part to the next, prescribed alterations in large production runs.
- Efficiency minimizes the material wasted and minimizes the amount of rework, thus saving considerable time and money.
- Versatility: This process can work on almost all metals, plastics, composites, and even ceramics.
What is the Precision Machining Process?
Precision machining is normally a 2 step process, each of which is very crucial for the accuracy and detail. The general steps are as follows:
1. Inception: design the graphical method
It begins with an inception stage where the engineers design the component either in the form of a blueprint or CAD model with the tiniest of details. It includes the critical dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications.
2. Machine Programming: convert CAD to CAM
The CAD model then has to be converted to a CAM program. A CAM program then tells the CNC machine how it has to move, cut, and shape the material. This programming is very crucial for the accomplishment of accuracy and efficiency during the machine operation.
3. Material Selection and Preparation
Correct selection of material is very important since it would determine the performance of the final product. It includes the functional role of the component and all environmental factors. The desire for good durability, which the selected material has in store, is prepared by cutting it to a size that is good enough for machining.
4. Follow the programmed instructions:
The core of the process involves automation, where the CNC machine follows programmed instructions for further removal of material from a workpiece. It could also imply a few basic techniques, such as:
- Turning—Removal of material as the workpiece rotates.
- Milling—Removal of material from a workpiece using rotary cutters along various axes.
- Drilling—Creation of holes or cylindrical cuts with the use of a rotating drill bit.
- Grinding—The process of surface finishing to an accurate, smooth finish.
5. Inspection and Quality Control
The component is critically inspected after machining to ensure that it has reached the necessary range for tolerating limits and dimensions at the sophisticated measuring level, such as CMM-coordinate-measuring machines or laser scanners, which largely take measures for accuracy.
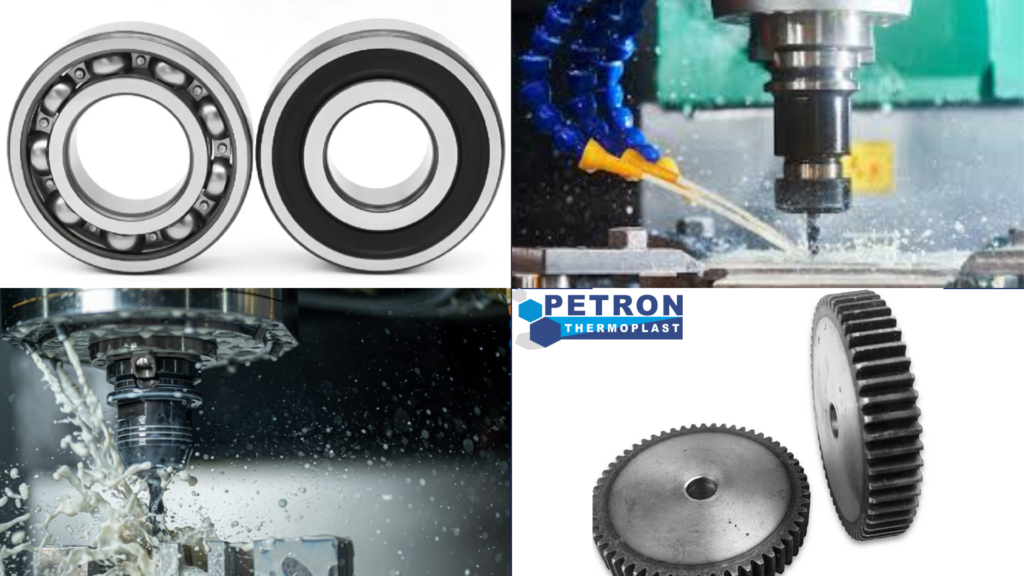

What does Precision Machining Comprise?
In this process of precision machining, there are a number of machining components and tools that are used. Basically, in understanding how the whole process works, it is important to learn about these elements of precision machining, which deliver this great degree of accuracy.
1. CNC Machines
CNC Machining is the backbone of precision machining. These computer-controlled machines can perform several operations with unsurpassed accuracy. These include:
- CNC lathes: complete turning in the fabrication of cylindrical parts
- CNC milling machines cut and shape more complex parts using a multiplicity of axes.
- CNC Routers: makes cuts and shapes in wood, plastic, and aluminum
2. Cutting Tools
Certainly, it is the tools that provide the heart for any machining. From high-speed steel, carbides, and even ceramics, all are made from the basic raw materials and developed to withstand the toughest of conditions yet maintain sharpness at the edge for precision in cuts.
3. Workholding Devices
Workholding devices are those devices by which, after fixing, holding the workpiece during the operation and ensuring that the workpiece remains in a stable and correct position. Examples include:
- Vices: Clamping devices to clamp the workpiece.
- Chucks: mounted on the lathe machine to clamp workpieces.
- Fixtures: Special machines designed for holding specific workpieces.
4. Coolant and Lubricant
The coolants and lubricants maintain the heat generated within the system at a minimum and lubricate friction during the workpiece machining. They can also flush the generated chip and swarf so that clean chips can be obtained and the lifetime of cutting tools improved in the process.
5. Metrology Applications
Metrology is the science that assures the measurement and inspection of machined components, using tools like micrometers, calipers, gauges, and CMMs to assure product specifications. Precision machining, a core role in modern manufacturing, is that very basic entity defining that one can get a high-strength, minutely detailed, and accuracy-assured component, be it from the aerospace and automotive industry or the vast areas of medicine. Just understand the procedure, uses, and elements concerned in the process, and you will appreciate how much detail and skill this trade involves to come up with a functional and flawless part. In all these industries, precision machining ensures that every part is apt to perform its activity with accuracy and full reliability.
Suitable Materials for Precision Machining
Frequent materials used for precision machining include:
Metals and alloys
- Stainless steel
- Steel
- Titanium
- Tool steel
- Exotic alloys
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Bronze
- Carbon steel
- Copper
Plastics and Other Non-Metals
- Polyamide (PA)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
- Polyoxymethylene (POM)
- Glass
- Graphite
Components of Precision Machining made by Petron Thermoplast
Petron thermoplast ensure the provision of integral parts of mechanical systems designed to operate with exacting accuracy and consistency. Here are some common precision machining parts made by Petron Thermoplast.
- Bearings
- Gears
- Shafts
- Couplings
- Bushings and sleeves
- Springs
- Fasteners
- Seals and gaskets
- Pins and dowels
- Actuators and sensors
Why choose Petron Thermoplast as the Best Choice for Precision Machining Parts?
In today’s modern world, choose Petron Thermoplast as your trusted partner for precision machining. In this era, where quality, precision, and customer satisfaction are our top priorities as manufacturers, Petron Thermoplast stands with 10 years of trust and goodwill in the manufacturing industry market. We assure you that we provide you:
Unrivaled Expertise: Having produced in precision machining for many years, Petron Thermoplast has, through an accumulation of such experience, rare skills to deliver parts with high standards of accuracy and quality. We leverage CAD/CAM/CAE technology with sophisticated CNC machinery into the latest frontier in technology support in the main and enable each component to be produced at the level of ultimate top quality.
Custom Solutions: At Petron Thermoplast, we know each job is different. We would be happy to work with you to provide a tailored machining solution for your specific needs, no matter how complicated.
Quality Guarantee: With our comprehensive quality control, every part produced will meet the tight tolerances and exact specifications that you require.
Full-Service Support: Our highly skilled, experienced team provides complete support at every step in your project.
Wide Variety of Materials: We provide various types of metals, plastics, and composites that fit your needs.
On-Time Delivery: We assure on-time delivery in your every project.
Competitive Prices: Petron Thermoplast assures to provide you every deal at the best price.
Conclusion
In this advanced technological world, precision machining must be an important skill. CNC precision machining takes this a notch higher by ensuring unparalleled accuracy and easing the whole manufacturing process. Hence, precision machining has become a must-have part of modern industrialization, where accuracy and consistency are the baselines in complex machine manufacturing. CNC precision machining has become a necessity for the rapid growth of manufacturers.